FAQ
Does it support running on Windows / Mac?
Not yet, but there are plans to support it in the future.(ISSUE-151)
Does it support running on lower kernel versions?
Currently, it supports the minimum kernel version: 3.10.0-957, but some features may be missing on lower kernel versions.
Currently, 3.* kernel versions do not support filtering traffic by container ID/container name and cannot automatically associate traffic before and after NAT.
Does it support running on Linux in WSL?
Theoretically yes, but Linux distributions on WSL usually do not include Linux headers by default, which kyanos depends on. You may need to modify the compilation options to manually compile the kernel. For specific methods, refer to: Enabling eBPF/XDP for Kernel Tinkering on WSL2
Can it run in a container/Pod?
It must run in a privileged mode container/Pod.
When using the --pod-name option, the "can not find any running pod by name xxx" log appears
Kyanos must be running on the same host as the target Pod.
can't find btf file to load! log appears during operation
This may be because your system lacks the BTF file. You can manually download the BTF file that matches your kernel from here: https://mirrors.openanolis.cn/coolbpf/btf/ and https://github.com/aquasecurity/btfhub-archive/. Specify the downloaded BTF file with the --btf option when starting kyanos.
How to understand the visualization of kernel time in the watch results?
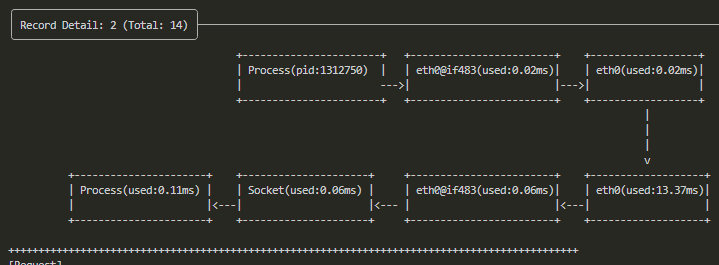
In the image, eth0@if483 is the container NIC, and eth0 is the host NIC.
The upper part of the image shows the request from the process sending to the NIC, and the lower part shows the response from the NIC to the process.
Incorrect terminal table colors after running (e.g., unable to select records in the table)
Check if there is a Your terminal does not support 256 colors, ui may display incorrectly log. If so, it means the terminal color configuration is incorrect. Kyanos requires a 256-color terminal.
Use the following command to list all terminal types supported by the system and their supported color bits:
for T in `find /usr/share/terminfo -type f -printf '%f '`;do echo "$T `tput -T $T colors`";done|sort -nk2|tail -n20Example output:
Eterm-88color 88
rxvt-88color 88
xterm-88color 88
xterm+88color 88
Eterm-256color 256
gnome-256color 256
iTerm.app 256
konsole-256color 256
...The $TERM variable represents the current terminal type, which can be viewed using the echo $TERM command.
You can change it to 256 colors by modifying the ~/.bashrc file. Add the following code to the .bashrc file:
case "$TERM" in
xterm)
export TERM=xterm-256color
;;
screen)
export TERM=screen-256color
;;
esac